The cultivation of cocoa requires the shade of special trees, generating an agroforestry system that resembles the forest original, and has served as a support to many families in the fields of cultivation and in the process of transformation into cocoa chocolate.
Taxonomic classification:
Exceptional, they reach 50 depending on the size of ear.
The ear matures at 5 or 7 months, from fertilization. The Cocoa clones are classified using characters from the cob as:
Color:
Before maturity, the color of the cob can be green, red violet and green partially pigmented red-violet, according to the clone.
The Amazonian Foreigners always present green cobs. The Criollos and Trinitarios have red or green color. In mature ears, the green color changes to yellow and the red-violet color changes to orange.

It is variable between 10 to 30 cm in length and 7 to 12 cm in diameter. The thickness of the shell is 1 to 2 cm.

The fruits by their form are classified in: Angoleta, Amelonado, Cundeamor and Calabacillo.
| Angoleta | Cundeamor | Amelonado | Calabacillo |
 |
 |
 |
 |
The cocoa seed or almond is bean-shaped, with a 2 to 3 cm length, covered with a flavor mucilaginous pulp bittersweet. The germination process starts when the cob reaches its physiological maturity. The weight varies from 2 to 3.7 gr depending on the genetics of the clone. The length of the seeds varies from 20 to 30 mm and of width between 10 to 17 mm.
The shape of the seed also varies a lot from triangular, ovoid, elongated or rounded, flat or crushed.
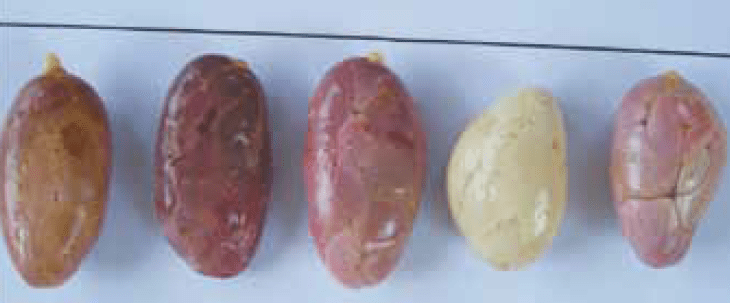
Cocoa is an allogamous species with 95% pollination crusade. By genetics they are classified into three major groups: Creoles, Outsiders and a mixture of them that is called Trinitarios.
Criollo cacao
Genetic type of cocoa whose crop was dispersed from Mexico to Central America, of high quality and pleasant taste. Has been domesticated and adapted to different areas, the plant is very delicate, of low productivity and susceptible to diseases. It can be distinguished by the architecture of a weak tree, large, dark leaves, new sprouts are pale green, staminodios of intense red color, the type of ear is rustic of thin shell and cundeamor shape.
The almond is white, with chocolate flavor and aroma, superior to any type of cocoa in the world. It has great Demand in the national and international market.cob is rustic of thin shell and cundeamor shape. The almond is white, with chocolate flavor and aroma, superior to any type of cocoa in the world. It has great demand in the national and international market.
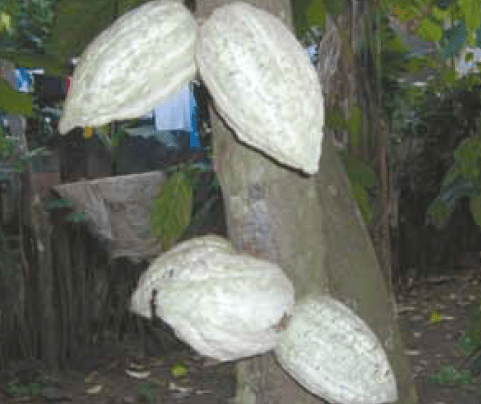

Originating in the Amazon Basin, they are robust trees and large, small leaves, ears type amelonado, hard husk, thick and smooth, flattened and pigmented almonds, pest tolerant and adapt very well to different environments.
The taste of almonds is very ordinary and bitter.

It is the cocoa that is most cultivated in America. It is considered as a natural hybrid from the first two types of cocoa. By this reason they present a great variability and it is where they have arisen excellent genotypes of great robustness, resistance to pests and higher performance. Trinitarios comes from Trinidad, Island of the Antilles Minors where the English founded a famous institute of cocoa research, Imperial College Station.

Stages of cocoa processing:
HARVEST
The cocoa gives production to the third or fourth year of its establishment.
All year round with production peaks between April and June and between November and dicember.
With a good seed and applying appropriate techniques you can take 15 to 20 quintals per manzana.
The ears take time to mature between 5 and 7 months when they observe in them a change of color. The cut is made with a lot careful not to damage the floral bearing. Tools are used as: hawks and short sharp machetes.
The break of the cob is done by hitting it with an object to remove the grain and separate the mucilage.
A traditional practice is to wash the grain and put it to dry immediately. In this process, cocoa loses quality.

Fermentation is very important for the quality of cocoa. He obtains the characteristic chocolate aroma, flavor and color of the variety or clone used.
The fermentation lasts between 5 and 7 days when the temperature rises up to 45 degrees and the embryo dies.
Baba beans are placed in wooden crates and they are moving once a day to have an even fermentation.

The drying of the cocoa is done in wooden boxes, shakers or concrete patios placed in the sun or in artificial dryers like stoves. With good sun the drying lasts a week to have the 7 at 8% humidity in the grain. It is packed in jute bags.

With the cocoa after the fermentation and drying, the roasting, alkalizing and grinding processes are carried out to then proceed to the chocolate production.

Cocoa